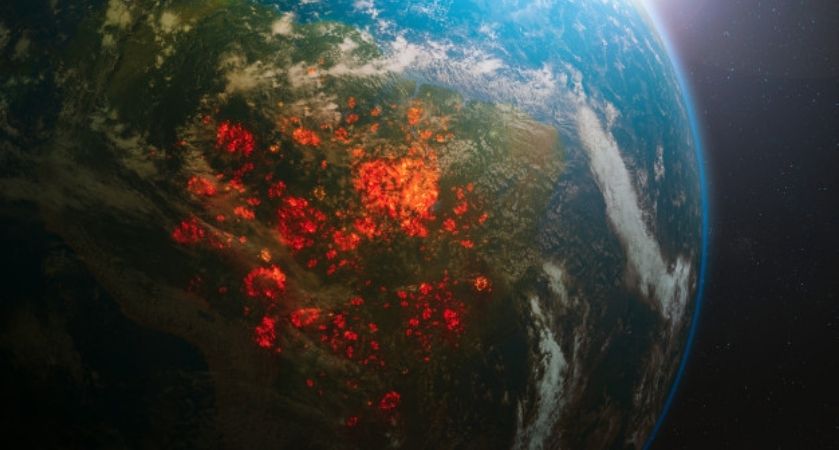
Climate change, along with the loss of biodiversity, is one of the greatest challenges our world has ever faced. The increase in global average temperatures is in fact compromising our climate and these effects, if not countered with concrete actions, are destined to worsen in the coming years.
It is only now that we are given the opportunity to act and prevent irreparable changes in the future. If we want to contain the global temperature rise below 1.5 ° C compared to pre-industrial levels, man-made greenhouse gas emissions must necessarily decrease by at least 50% by 2030 (Source: IPCC ).
On this page you will find a summary of the climate crisis, what is causing it and what you can do to alleviate its consequences.
What is Climate Change?
The climate is naturally variable. The lack of regularity in the seasons from year to year is an example of this variability caused by many interacting factors (changes in ocean currents, volcanic activity, solar radiation, major climatic events such as El Niño, Indian monsoons and so on. Street).
Climate change therefore represents a significant and lasting variation in the statistical distribution of meteorological trends and can occur over decades or millions of years. The change occurs in changes in average weather conditions (for example, average wet season start date in the tropics) or in changes in the frequency of extreme weather events such as floods, droughts and storms.
The changes in the orbital patterns of the sun, called “Milanković Cycles”, are the most significant factor of climate change: in the last 40 thousand years they have been the main driving force of the last four cycles of glaciations and warm periods. However, the Earth’s climate has changed significantly over the past 150 years and it is extremely important to understand what causes this anomalous variation in such a short period of time.
Global Warming of the Planet
Many studies have conclusively shown that global average temperatures began to rise from the second half of the 19th century. This phenomenon, commonly called “global warming”, is actually defined by scientists and experts as “anthropogenic climate change” because it is caused by human activities (in particular by CO 2 emissions into the atmosphere due to the use of fossil fuels).
The IPCC special report on global warming of 1.5ºC, published in October 2018, showed that human activities have already had a significant impact on global temperatures and that warming is continuously increasing: “It is estimated that human activities have caused about 1.0 °C of global warming above pre-industrial levels, with a possible range of 0.8 ° C to 1.2 ° C. If it continues to increase at the current rate, global warming will likely reach 1.5 ° C between 2030 and 2052″.
Although a 1.5 °C temperature rise may seem insignificant, the aforementioned IPCC report demonstrates how this could lead to serious consequences.
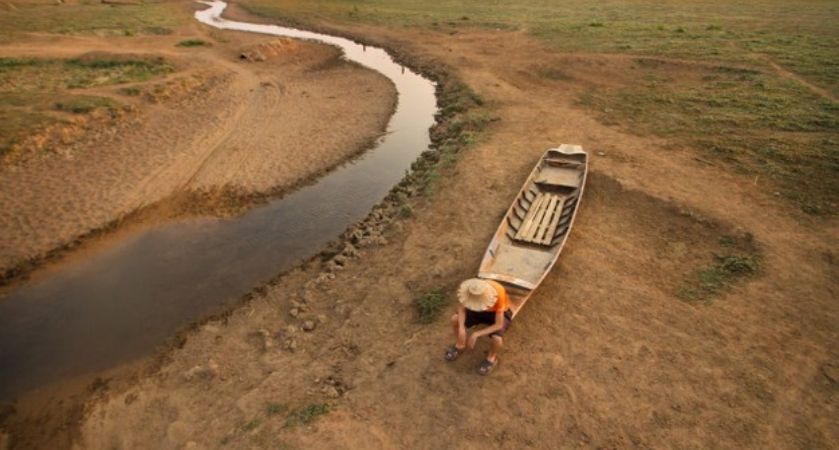

The Causes of Climate Change
Temperatures on Earth are liveable thanks to a natural process called the “greenhouse effect”. When the sun’s radiation reaches our atmosphere, some are reflected back into space while others pass and are absorbed by the Earth, causing the surface of our planet to warm up. However, the earth’s heat is radiated outwards and absorbed by the gases present in the earth’s atmosphere, called “greenhouse gases”. Greenhouse gases prevent heat being dissipated again in space and maintain the average temperature of the Earth to approximately +15 ° C instead of at -18 ° C.
Over the past century, humans have released more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, thereby increasing its effect. Many of these gases come from the use of fossil fuels used in factories, means of transport and agriculture. Carbon dioxide is the gas most responsible for overheating, especially because it is most present. Other greenhouse gases are methane, nitrous oxide, CFCs, HCFCs and methyl bromide.
Global warming is further aggravated by the loss of forests and wetlands, responsible for storing CO 2: it is estimated that more than 32,000 hectares of tropical rainforest are felled every day for the timber industry or for the construction of agricultural fields.
The Consequences
Climate change is altering not only the environment we live in, but also the economy, communities and, last but not least, our health. If we do not change our lifestyle and our energy consumption to keep the global temperature rise below 1.5 ° C, the consequences will be dire.
The scenario that the IPCC special report describes after careful scientific studies predicts serious effects. Some of these include:
- Melting of glaciers and rising sea levels due to water expansion at warmer temperatures.
- Increased intensity and frequency of extreme weather phenomena such as hurricanes, floods, droughts and storms.
- Water scarcity in some areas, desertification and decreased crop yields with consequent exacerbation of existing regional tensions and further violent conflicts.
- Less reliable and predictable seasons, difficult long-term planning and more likely to fail for crops resulting in food shortages.
- Destruction of coral reefs, ocean acidification and decreased yields in the fishing industry.
- Loss of habitats, biodiversity, ecosystems and species extinction.
- Changes in the geographical range of species.
- Increased disease, particularly malaria and dengue fever, as mosquitoes are able to survive in higher latitudes and altitudes.
In the past, it was thought that fighting climate change would require a huge financial cost, which could explain why many countries have been reluctant to take preventive measures. To date, the economic impact of climate change is considered enormous: global warming is a situation of loss for all and it is in the interest of all of us to prevent it!